What You Need to Know About Voltage Compatibility
Alright, let’s talk about something that can make or break your travel experience: voltage compatibility. If you're planning a trip to the UK or anywhere in Europe, it’s crucial to understand the voltage differences and how they affect your devices. For instance, if your gadgets are compatible with the local voltage—230 volts—you’ll only need a three-pin adapter to plug them in. But here's the catch: not all devices are built the same, so it’s worth double-checking before you pack.
UK Voltage Standards: What You Should Expect
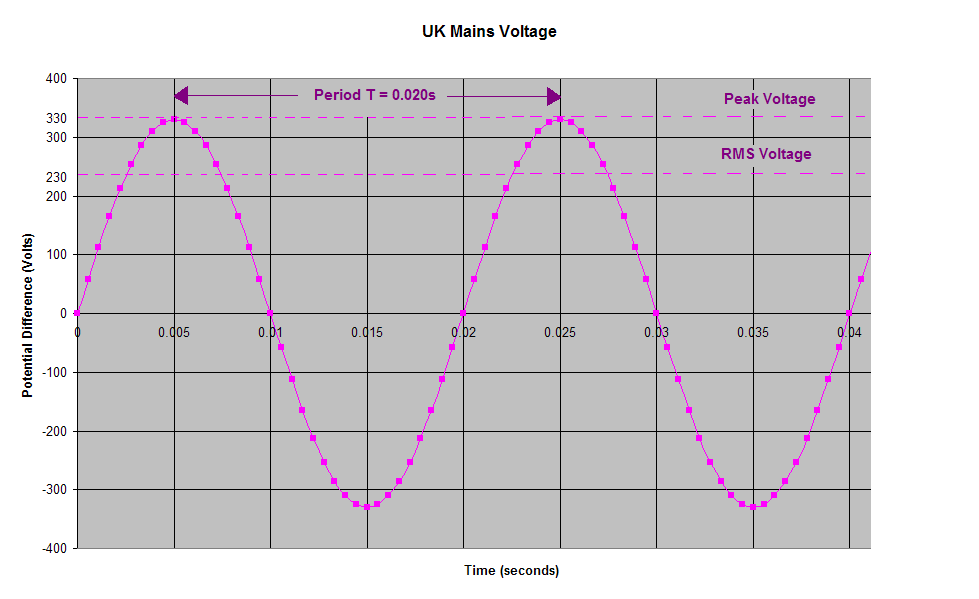
Let me break it down for you. Just like the rest of Europe, the UK operates on a voltage of 230 volts and a frequency of 50 hertz. But here’s the thing: this doesn’t mean the voltage is fixed at exactly 230 volts. In reality, the voltage can fluctuate between 216 volts and 253 volts. That’s why manufacturers build in a safety margin to ensure your appliances won’t be affected by minor fluctuations. So, if you’re bringing a device from the US, which typically runs on 120 volts, you’ll definitely need a voltage converter in addition to an adapter.
Global Voltage and Frequency Overview
Take a look at the bigger picture. Across most countries, the mains supply generally falls between 220 and 240 volts, with frequencies of either 50 or 60 hertz. This means that if your device can handle that range, you’re good to go in most parts of the world. Interestingly, types A and C electric plugs are the most commonly used worldwide, making them a safe bet when packing for international travel. But don’t assume compatibility—always verify your device’s specifications before you leave.
Read also:How To Get Started With Discord And Make The Most Of It
How Smart Grids Are Revolutionizing Voltage Management
Now, let’s dive into the future of electricity. The implementation of smart grid technologies is changing the game when it comes to voltage management. These advanced systems help optimize energy distribution, reduce waste, and improve reliability. For instance, in the UK, the traditional single-phase mains power supply voltage was 240 volts, while in Europe, it was 220 volts. But guess what? As of 2003, both regions have harmonized their voltages to a nominal 230 volts. This change might sound small, but it has a big impact on how we design and use electrical equipment.
Industrial vs. Household Voltage Standards
When it comes to industrial machinery, the story changes slightly. For years, mainland Western Europe relied on a 380-volt, three-phase electricity supply, while the UK used 415 volts. These higher voltages are essential for powering large-scale equipment, but they require specialized plugs and sockets. On the other hand, households operate on single-phase power, which is much safer and more efficient for everyday use. The good news is that modern appliances are designed to handle a wide range of voltages, so you don’t have to worry too much about compatibility issues at home.
Direct Current vs. Alternating Current
Let’s take a moment to talk about the difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). DC is the type of electricity produced by batteries, where the current flows in one direction. AC, on the other hand, is what powers our homes and businesses through the electrical grid. The UK’s mains electricity is an alternating current voltage at a frequency of 50 hertz, which is perfect for most household appliances. But if you’re using devices that require DC, like some laptops or smartphones, you’ll need a power adapter to convert the current.
Tips for Travelers: Adapters, Converters, and Voltage Safety
Here’s a quick tip for travelers: always check if your device has a voltage switch on the back. Many desktop computers and other electronics have this feature, allowing you to toggle between 120 volts and 240 volts. If your device doesn’t have a switch, you might need to replace the power supply unit (PSU) or buy a new power cord. Either way, it’s a small investment that can save you a lot of trouble down the road.
Now, let’s talk about safety. Voltage fluctuations can happen anywhere, and they can cause problems with your devices, especially sensitive electronics like EV chargers or solar panels. If you notice your lights dimming or flickering, it’s a sign that something’s off. In these cases, it’s best to contact your local utility company and report the issue. They’ll be able to help you figure out what’s going on and how to fix it.
Harmonization and Future Developments
As we move forward, the harmonization of voltage standards is becoming more important. Since 2003, Europe and the UK have aligned their voltages at 230 volts, making it easier to use appliances across borders. This change might seem minor, but it reflects a broader trend toward standardization and efficiency. And with the rise of renewable energy sources like wind power, which contributed 15% of the UK’s electricity generation in 2017, the future of electricity looks brighter than ever.
Read also:Lee Dong Wooks Love Story A Closer Look At His Relationship With Jo Bo Ah
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding voltage compatibility and electrical standards is key to ensuring your devices work seamlessly wherever you go. Whether you’re traveling for business or pleasure, take the time to research the local voltage requirements and pack the right adapters and converters. By doing so, you’ll avoid costly mistakes and enjoy a stress-free experience. Stay safe, stay informed, and keep those gadgets charged!